If you ever tried to communicate STM32 microcontroller over RS485 and got confused about wiring or code, this post is for you. In this tutorial, I’ll show how to implement Modbus RS485 communication in STM32 using TTL to RS485 converter module and USB to RS485 converter connected to a PC. We will see how data can be send and receive through this setup and displayed in Docklight or any serial terminal.
This project is simple but very useful when you want to make Modbus or RS485 communication between microcontrollers, PLCs, or sensors. Let’s get started step by step.
What is RS485 and Why We Use It?
RS485 is a differential communication protocol that allows data transmission over long distances and with multiple devices connected on same bus. Unlike UART (TTL level), RS485 uses A and B differential lines which makes it very noise resistant and suitable for industrial environments.
You can connect many slave devices on single RS485 line and it supports half-duplex communication. In half duplex mode, both transmitter and receiver share same pair of wires but not simultaneously.
That’s why we control a pin called DE (Driver Enable) or sometimes RE (Receiver Enable) to switch between transmit and receive mode.
Hardware Setup
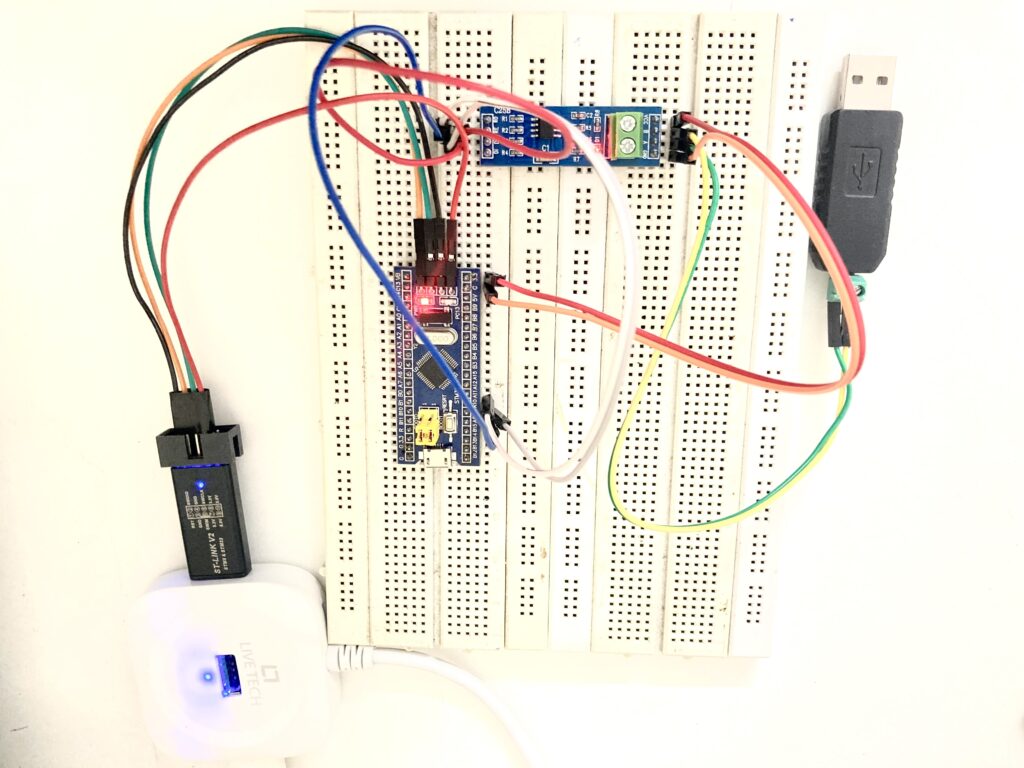
For this project, I used following hardware components:
- STM32F103C8T6 (Blue Pill board)
- TTL to RS485 converter module (like MAX485)
- USB to RS485 converter (for PC side)
- PC with Docklight or any serial terminal software
Connection diagram:
| STM32 Pin | TTL to RS485 Module | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PA9 (TX1) | DI | UART TX |
| PA10 (RX1) | RO | UART RX |
| PA8 | DE/RE | RS485 Direction Control |
| GND | GND | Common Ground |
| 5V or 3.3V | VCC | Power |
On the PC side, connect USB to RS485 converter to your computer. The converter usually has A and B lines. Connect these to A and B of the TTL-RS485 module.
Now open Docklight (or RealTerm / Modbus Poll / any serial monitor) on your PC, select correct COM port and baudrate (9600 baud in our case).
Working Principle
The STM32 will act as RS485 device which receives data from PC (via USB RS485) and simply echo back whatever it received. This helps verify our wiring and RS485 communication setup.
If the echo is working, then Modbus RTU can be implemented easily later.
Important Points Before Code
- DE pin control: We must set RS485 module to transmit mode when sending data and receive mode otherwise.
- UART Interrupt Receive: We use
HAL_UART_Receive_IT()to get continuous data reception. - Frame timeout: We detect end of frame by checking time difference between received bytes.
- LED blink: Just to show data activity on STM32 board.
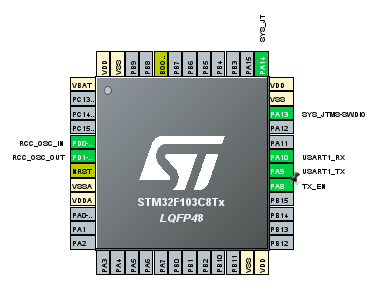
STM32CubeMX Configuration
Open STM32CubeMX and do following:
- Enable USART1 in asynchronous mode.
- Set baud rate to 9600, 8-bit, 1 stop bit, no parity.
- Configure PA8 as GPIO Output (for RS485 DE pin).
- Enable PC13 as LED output.
- Generate code for STM32 HAL.
Then add below C code into your main.c.
Complete STM32 RS485 Echo Code
Below is full working code example for RS485 echo on STM32. This will help you understand how to handle half duplex RS485 in STM32 using HAL library.
/* USER CODE BEGIN Header */
/**
******************************************************************************
* @file : main.c
* @brief : Main program body (RS485 Echo)
******************************************************************************
* @attention
* Copyright (c) 2025 STMicroelectronics.
* All rights reserved.
* This software component is licensed by ST under Ultimate Liberty license
* SLA0044.
******************************************************************************
*/
/* USER CODE END Header */
#include "main.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#define RS485_DE_GPIO_PORT GPIOA
#define RS485_DE_PIN GPIO_PIN_8
#define LED_GPIO_PORT GPIOC
#define LED_PIN GPIO_PIN_13
#define RX_BUF_SIZE 256
#define RS485_FRAME_TIMEOUT_MS 5
UART_HandleTypeDef huart1;
uint8_t rx_buf[RX_BUF_SIZE];
volatile uint16_t rx_len = 0;
volatile uint32_t last_rx_tick = 0;
volatile uint32_t led_blink_time = 0;
void SystemClock_Config(void);
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void);
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void);
void RS485_SetTx(void);
void RS485_SetRx(void);
void RS485_Send(uint8_t *pData, uint16_t size);
void Echo_ProcessFrame(uint8_t *frame, uint16_t len);
int main(void)
{
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
MX_GPIO_Init();
MX_USART1_UART_Init();
RS485_SetRx();
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &rx_buf[rx_len], 1);
while (1)
{
if (rx_len > 0)
{
uint32_t now = HAL_GetTick();
if ((now - last_rx_tick) >= RS485_FRAME_TIMEOUT_MS)
{
uint16_t len = rx_len;
rx_len = 0;
Echo_ProcessFrame(rx_buf, len);
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
led_blink_time = HAL_GetTick();
}
}
if (HAL_GetTick() - led_blink_time > 50)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
}
}
void RS485_SetTx(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RS485_DE_GPIO_PORT, RS485_DE_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
}
void RS485_SetRx(void)
{
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(RS485_DE_GPIO_PORT, RS485_DE_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
}
void RS485_Send(uint8_t *pData, uint16_t size)
{
RS485_SetTx();
HAL_Delay(1);
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, pData, size, HAL_MAX_DELAY);
while (__HAL_UART_GET_FLAG(&huart1, UART_FLAG_TC) == RESET);
HAL_Delay(2);
RS485_SetRx();
}
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
if (huart == &huart1)
{
rx_len++;
if (rx_len >= RX_BUF_SIZE) rx_len = RX_BUF_SIZE - 1;
last_rx_tick = HAL_GetTick();
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, &rx_buf[rx_len], 1);
}
}
void Echo_ProcessFrame(uint8_t *frame, uint16_t len)
{
if (len == 0) return;
RS485_Send(frame, len);
}
void SystemClock_Config(void)
{
RCC_OscInitTypeDef RCC_OscInitStruct = {0};
RCC_ClkInitTypeDef RCC_ClkInitStruct = {0};
__HAL_RCC_AFIO_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_PWR_CLK_ENABLE();
RCC_OscInitStruct.OscillatorType = RCC_OSCILLATORTYPE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.HSEState = RCC_HSE_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLState = RCC_PLL_ON;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLSource = RCC_PLLSOURCE_HSE;
RCC_OscInitStruct.PLL.PLLMUL = RCC_PLL_MUL9;
HAL_RCC_OscConfig(&RCC_OscInitStruct);
RCC_ClkInitStruct.ClockType = RCC_CLOCKTYPE_HCLK | RCC_CLOCKTYPE_SYSCLK |
RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK1 | RCC_CLOCKTYPE_PCLK2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.SYSCLKSource = RCC_SYSCLKSOURCE_PLLCLK;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.AHBCLKDivider = RCC_SYSCLK_DIV1;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB1CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV2;
RCC_ClkInitStruct.APB2CLKDivider = RCC_HCLK_DIV1;
HAL_RCC_ClockConfig(&RCC_ClkInitStruct, FLASH_LATENCY_2);
}
static void MX_USART1_UART_Init(void)
{
huart1.Instance = USART1;
huart1.Init.BaudRate = 9600;
huart1.Init.WordLength = UART_WORDLENGTH_8B;
huart1.Init.StopBits = UART_STOPBITS_1;
huart1.Init.Parity = UART_PARITY_NONE;
huart1.Init.Mode = UART_MODE_TX_RX;
huart1.Init.HwFlowCtl = UART_HWCONTROL_NONE;
huart1.Init.OverSampling = UART_OVERSAMPLING_16;
if (HAL_UART_Init(&huart1) != HAL_OK)
{
Error_Handler();
}
}
static void MX_GPIO_Init(void)
{
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct = {0};
__HAL_RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE();
__HAL_RCC_GPIOC_CLK_ENABLE();
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = RS485_DE_PIN;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_HIGH;
HAL_GPIO_Init(RS485_DE_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
RS485_SetRx();
GPIO_InitStruct.Pin = LED_PIN;
GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP;
GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_FREQ_LOW;
HAL_GPIO_Init(LED_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct);
}
void Error_Handler(void)
{
__disable_irq();
while (1)
{
HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(LED_GPIO_PORT, LED_PIN);
HAL_Delay(100);
}
}
Testing the RS485 Communication
After flashing above code into your STM32, open Docklight on your PC.
- Select correct COM port (USB RS485 converter).
- Baud rate = 9600, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity.
- Type any string (like
HELLO) and send. - You should receive the same data echoed back immediately.
If LED blinks when data received, your RS485 echo communication is successful.
Explanation of Main Code Sections
- RS485_SetTx() / RS485_SetRx():
Controls DE pin to enable transmitter or receiver. - HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback():
Called when one byte is received. It stores data in buffer and re-enables interrupt for next byte. - Echo_ProcessFrame():
When a frame is complete (detected by timeout), it sends back the same data. - RS485_Send():
Handles transmission with proper delay to allow DE pin stabilization. - LED indicator:
Turns off for 50ms on each message received, acts as RX activity indicator.
Expanding to Modbus RTU
This example is just an echo test but forms a solid base for Modbus RTU slave or master implementation. You can replace Echo_ProcessFrame() function with Modbus frame parser (like reading function code, address, CRC, etc.).
Many industrial devices use Modbus RTU over RS485, so mastering this setup is first step toward that.
Common Issues and Fixes
| Problem | Possible Reason | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| No data received | Wrong A/B connection | Swap A and B lines |
| Garbage characters | Baudrate mismatch | Set both sides to 9600 |
| No echo | DE pin not controlled properly | Check PA8 logic with oscilloscope |
| LED not blinking | GPIO config wrong | Verify PC13 direction output |
Summary
In this tutorial we learned:
- How RS485 works and why it’s better than UART for long-distance communication.
- How to connect STM32 with TTL to RS485 and USB RS485 converters.
- How to implement RS485 communication in STM32 using HAL and interrupts.
- Full working C code example with explanation.
- How to test communication using Docklight serial terminal.
This project is beginner friendly but gives clear understanding of half duplex RS485 communication which is widely used in industrial Modbus networks.
Conclusion
Now you can communicate between STM32 and PC or any other RS485 device using this simple setup. Once echo test is working, you can move further and add Modbus RTU slave stack or custom data protocol on top of it.
Hope this tutorial helps you. If you found it useful, share it with your friends or leave comment below. Keep experimenting with STM32 and RS485, it’s one of the most practical communication systems in embedded electronics.
Keywords:
stm32 rs485 tutorial, modbus rs485 stm32, rs485 communication in stm32, ttl to rs485 converter stm32, usb rs485 stm32 docklight, rs485 echo test stm32, modbus rtu stm32 hal example, stm32 uart rs485 communication, stm32 bluepill rs485 project.