Learn how to interface the MCP4921 12-bit Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) with a TI microcontroller using SPI and TI-RTOS driver libraries.
Introduction
In embedded systems, Digital-to-Analog Converters (DAC) play a vital role in converting digital signals into real-world analog voltages. Whether you’re building sensor simulators, waveform generators, or control systems, a reliable DAC interface is essential.
One of the most popular DACs for embedded applications is the Microchip MCP4921 — a 12-bit SPI-compatible DAC that provides high precision and simple interfacing.
When combined with Texas Instruments ( TI ) microcontrollers and the TI Driver Library ( TI-RTOS or SimpleLink SDK), you get a modular, portable, and maintainable solution for analog output generation.
- What the MCP4921 DAC is and how it works
- How to configure the SPI peripheral using TI driver framework
- How to send digital values to control analog voltage output
- Example C code for Code Composer Studio (CCS).
- How to calculate output voltage levels
- Applications of DACs in embedded design
What is MCP4921?
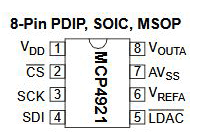
The MCP4921 is a single-channel, 12-bit Digital-to-Analog Converter from Microchip Technology. It takes a 12-bit digital value (0–4095) and converts it into a proportional analog voltage based on a reference voltage (Vref).
It supports SPI communication, which allows simple and high-speed interfacing with most microcontrollers, including TI’s MSP432, TM4C, CC32xx, and other cortex-M based devices.
Key Features
- 12-bit resolution (4096 discrete voltage steps)
- SPI-compatible serial interface (up to 20 MHz)
- Unipolar output from 0V to Vref
- Selectable gain (1× or 2× Vref)
- Shutdown mode for power saving
- Single-channel DAC A
The MCP4921 is perfect for generating variable analog signals directly from a microcontroller, no external PWM filtering or complicated timing is required.
MCP4921 Command Frame Format
Communication with the MCP4921 occurs via 16-bit SPI frames . Each frame carries configuration bits and a 12-bit DAC value.
| Bits | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 15 | C | Channel Select (0 = DAC A, 1 = DAC B; only A exists on MCP4921) |
| 14 | BUF | Vref Input Buffer (1 = Buffered, 0 = Unbuffered) |
| 13 | GA | Gain (1 = 1×Vref, 0 = 2×Vref) |
| 12 | SHDN | Shutdown (1 = Active, 0 = Power-down) |
| 11–0 | D11–D0 | 12-bit DAC data (0–4095) |
Example:
To output full-scale voltage with buffer enabled and 1× gain :
Command = 0b0011 1111 1111 1111 = 0x3FFF
Project Setup in Code Composer Studio (CCS)
Follow these steps to configure your project:
- Open Code Composer Studio (CCS)
- Import the SPI driver example from TI Resource Explorer under your device’s SDK.
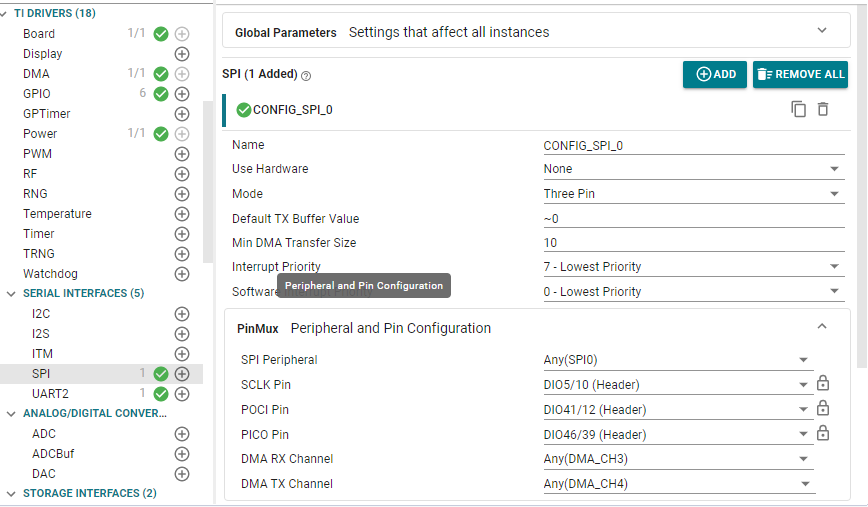
- Open SysConfig:
- Add an SPI peripheral named
CONFIG_SPI_0. - Set Four Pin Mode (CS Active Low)
- Assign appropriate pins:
SCLK = SPI Clock POCI = MOSI PICO = MISO (can be dummy) CSN = Chip Select
- Add an SPI peripheral named
- The MCP4921 is write-only, so MISO is not used. You can assign a dummy pin or leave it unconnected.
Include Required Header Files
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <ti/drivers/SPI.h>
#include <ti/drivers/GPIO.h>
#include <ti/drivers/dpl/ClockP.h>
#include "ti_drivers_config.h"These include TI driver libraries for SPI,GPIO, and timing management.
SPI Initialization for MCP4921
static SPI_Handle dacSpi;
void MCP4921_init(void)
{
SPI_Params spiParams;
SPI_Params_init(&spiParams);
spiParams.frameFormat = SPI_POL0_PHA0; // SPI Mode 0
spiParams.dataSize = 8; // 8-bit data per transfer
spiParams.bitRate = 1000000; // 1 MHz SPI clock
dacSpi = SPI_open(CONFIG_SPI_0, &spiParams);
if (dacSpi == NULL) {
while (1) { /* SPI initialization failed */ }
}
}
- SPI Mode 0 (CPOL=0, CPHA=0) matches MCP4921’s timing requirements.
- Bit rate of 1 MHz is safe for all TI MCUs.
- 8-bit transfer size ensures we can send 16-bit data in two bytes.
Writing a value to the MCP4921 DAC
bool MCP4921_write(uint16_t value)
{
SPI_Transaction trans;
uint8_t txBuf[2];
if (value > 0x0FFF) value = 0x0FFF; // Limit to 12-bit max
// Command bits: BUF=1, GA=1 (1xVref), SHDN=1 (Active)
uint16_t command = (0x3 << 12) | value;
txBuf[0] = (uint8_t)(command >> 8);
txBuf[1] = (uint8_t)(command & 0xFF);
trans.count = 2;
trans.txBuf = txBuf;
trans.rxBuf = NULL;
return SPI_transfer(dacSpi, &trans);
}
This function constructs the proper command frame and transmits it to the DAC.
Setting BUF=1, GA=1, and SHDN=1 ensures the DAC operates normally with buffered Vref and unity gain.
Main application [Gradual Output Changes]
void *mainThread(void *arg0)
{
SPI_init();
GPIO_init();
MCP4921_init();
const int percents[] = {0, 25, 50, 75, 100};
const int nSteps = sizeof(percents) / sizeof(percents[0]);
const uint16_t FULL = 4095;
const int delay_ms = 2000; // 2 seconds
while (1) {
for (int i = 0; i < nSteps; ++i) {
uint32_t code = (percents[i] * FULL + 50U) / 100U;
MCP4921_write((uint16_t)code);
ClockP_sleep(delay_ms / 1000);
ClockP_usleep((delay_ms % 1000) * 1000);
}
}
}
This loop sending output voltages corresponding to 0%, 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100% of full-scale, pausing 2 seconds between changes.
Calculating Output Voltage
For a reference voltage (Vref) of 3.3V: VOUT= DAC_CODE4095 × VREFV_{OUT} = \frac{DAC\_CODE}{4095} \times V_{REF}VOUT=4095DAC_CODE×VREF
| Percentage | DAC Code | Output Voltage |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 0 | 0.00 V |
| 25% | 1024 | ≈ 0.825 V |
| 50% | 2048 | ≈ 1.65 V |
| 75% | 3072 | ≈ 2.47 V |
| 100% | 4095 | ≈ 3.30 V |
If you need a 0–10V output range, you can buffer the DAC output through an op-amp configured as a non-inverting amplifier with gain = 3.03.
Practical applications of MCP4921 with TI Microcontrollers
- Analog Sensor Simulation – Generate adjustable analog voltages to emulate temperature sensors, pressure sensors, etc.
- Waveform Generation – Use a timer interrupt to write DAC values from a sine lookup table for analog waveform synthesis.
- 0–10V Control Output – With an op-amp stage,generate standard 0–10V control signals for industrial PLCs.
- Data Acquisition Systems – Output reference voltages or scaling factors.
- Audio or Signal Output – Combine with DMA for high-speed DAC streaming applications.
Troubleshootings
| Issue | Possible Cause | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| No output voltage | CS pin misconfigured | Verify active low chip select |
| Wrong voltage | SPI mode mismatch | Use SPI Mode 0 (CPOL=0, CPHA =0) |
| Output stuck at 0V | SHDN bit not set | Set SHDN =1 in command |
| No communication | Wiring error | Check MOSI and CLK continuity |
| Noisy output | Missing decoupling | Add 0.1 µF capacitor on Vref pin |
Ideas
- Use DMA with SPI for continuous waveform output
- Implement voltage ramp generation for motor control testing
- Integrate With RTOS Tasks to manage multiple DAC channels (using MCP4922 for dual outputs)
- Store DAC patterns in Flash or SD card for playback systems
Performance and Accuracy
The MCP4921 provides:
- 12-bit resolution ( ≈ 0.8 mV per step at 3.3V)
- ±2 LSB integral nonlinearity (INL)
- Low noise and fast settling (4.5 µs typical)
When used with TI microcontrollers, the SPI driver ensures consistent timing, error handling, and scalability.
Example Hardware Connection (SPI Wiring)
| TI MCU Pin | MCP4921 Pin | Function |
|---|---|---|
| SPI MOSI | SDI | Serial Data Input |
| SPI SCLK | SCK | Serial Clock |
| SPI CS | CS | Chip Select (Active Low) |
| GND | Vss | Ground |
| 3.3V | Vdd | Power Supply |
| 3.3V | Vref | Reference Voltage |
| Output | Vout | Analog Voltage Output |
Note: Connect a 0.1 µF capacitor between Vref and GND for stability.
Conclusion
The MCP4921 DAC is a reliable, cost-effective solution for adding analog output capability to TI microcontrollers.
Using SPI communication and TI driver libraries, you can easily produce accurate analog voltages with minimal code.
From simple voltage control to complex waveform generation, this interface serves as a powerful foundation for advanced embedded system applications .
Q1: What SPI mode does MCP4921 use?
A: MCP4921 uses SPI Mode 0 (CPOL=0, CPHA=0).
Q2: What is the output voltage range of MCP4921?
A: 0V to Vref (typically 3.3V or 5V, depending on your setup).
Q3: How to calculate DAC output voltage?
Vout = (DAC\_Value / 4095) × Vref
Keywords:
MCP4921 SPI, MCP4921 DAC example, TI microcontroller DAC interface, SPI DAC tutorial, MCP4921 TI RTOS, DAC code example, Digital to Analog converter TI, Code Composer Studio DAC, 12-bit DAC interfacing, embedded DAC control
Secondary Keywords:
DAC MCP4921 code, SPI mode 0 example, DAC output voltage, TI driver SPI example, TI CCS SPI DAC, analog voltage generation